虚弱 题解
E_firework
2022-07-22 18:36:55
先简单翻译一下题意:
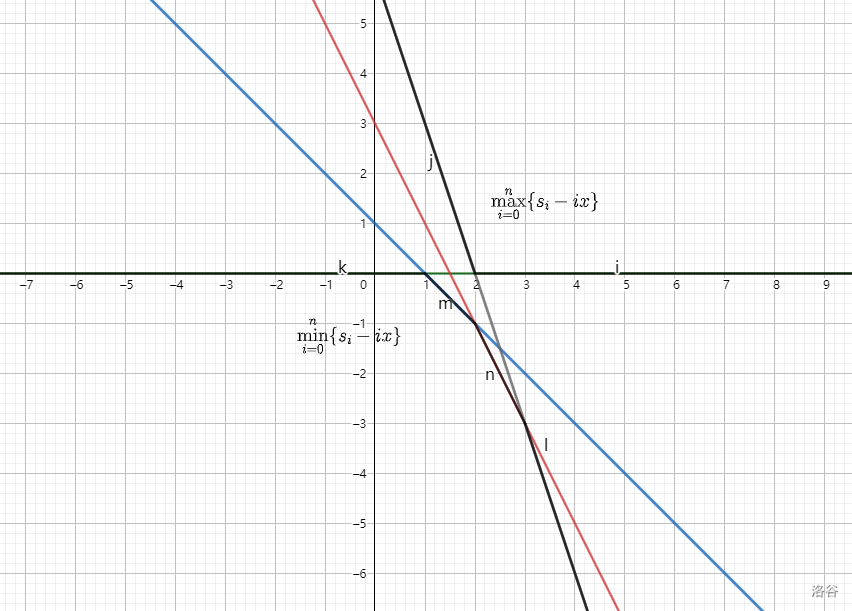
上面的式子变形一下,就是 $\left|(s_i-ix)-(s_j-jx)\right|\le ans$,问题可以转化为求$\max\limits_{i=0}^n\{s_i-ix\}-\min\limits_{i=0}^n\{s_i-ix\}$ 的最小值,发现括号中的式子是关于 $x$ 的一次函数,只需维护所有函数的上边缘和下边缘,可以用单调栈,显然最优解只会在拐点出现,枚举即可。
样例的图:
Code:
```cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
#define max(i, j) (i > j ? i : j)
#define min(i, j) (i < j ? i : j)
#define mes(s, x) memset(s, x, sizeof(s))
using namespace std;
inline LL read(){char c;c = getchar();while(!(('0' <= c && c <= '9') || c == '-')) c = getchar();bool flag = 0;if(c == '-'){flag = 1;c = getchar();}LL tot = 0;while('0' <= c && c <= '9'){tot = 10 * tot + c - '0';c = getchar();}return flag ? -tot : tot;}
int a[200005], stk1[200005], cnt1, stk2[200005], cnt2;
LL s[200005];
double solve(int i, int j){
return (s[i] - s[j]) * 1.0 / (i - j);
}
int main(){
int n = read();
if(n == 1){
printf("%.6lf", 0);
return 0;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = read(), s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i];
double ans = 2000000000;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
while(cnt1 >= 2 && solve(stk1[cnt1 - 1], stk1[cnt1]) >= solve(stk1[cnt1 - 1], i)) cnt1--;
stk1[++cnt1] = i;
}
for(int i = n; i >= 0; i--){
while(cnt2 >= 2 && solve(stk2[cnt2 - 1], stk2[cnt2]) >= solve(stk2[cnt2 - 1], i)) cnt2--;
stk2[++cnt2] = i;
}
double x;
for(int i = 1, j = 1; i < cnt1 || j < cnt2; ){
if(i != cnt1 && (j == cnt2 || solve(stk1[i], stk1[i + 1]) < solve(stk2[j], stk2[j + 1]))){
x = solve(stk1[i], stk1[i + 1]);
i++;
}else{
x = solve(stk2[j], stk2[j + 1]);
j++;
}
ans = min(ans, fabs(s[stk1[i]] - stk1[i] * x - (s[stk2[j]] - stk2[j] * x)));
}
printf("%.6lf", ans);
return 0;
}
```
顺带一提,C 也有线性的做法,但是要用 manacher 算法。